Informação

The type of review to be conducted depends on the question to be answered. For example, it is possible to answer the question, “Which research on the sustainability of employment for people with intellectual disabilities has been published internationally between 2010 and 2020” with the bibliometric review method (Taubner et al.,2022). The following table shows the types of reviews (HSL, 2024). Examining the review types allows you to determine the most appropriate review type for your research question. Using two or more review types to answer some of the questions of the studies may be possible (Grant & Booth, 2009). For example, when conducting research on the effectiveness of trauma intervention programs in the last ten years, it is possible to systematically analyze all the studies conducted in the last ten years and then calculate the impact value by meta-analysis of the numerical data obtained. In this case, systematic review and meta-analysis methods are used together. It is possible to conduct mixed design reviews, as in the example (Taubner et al.,2022).
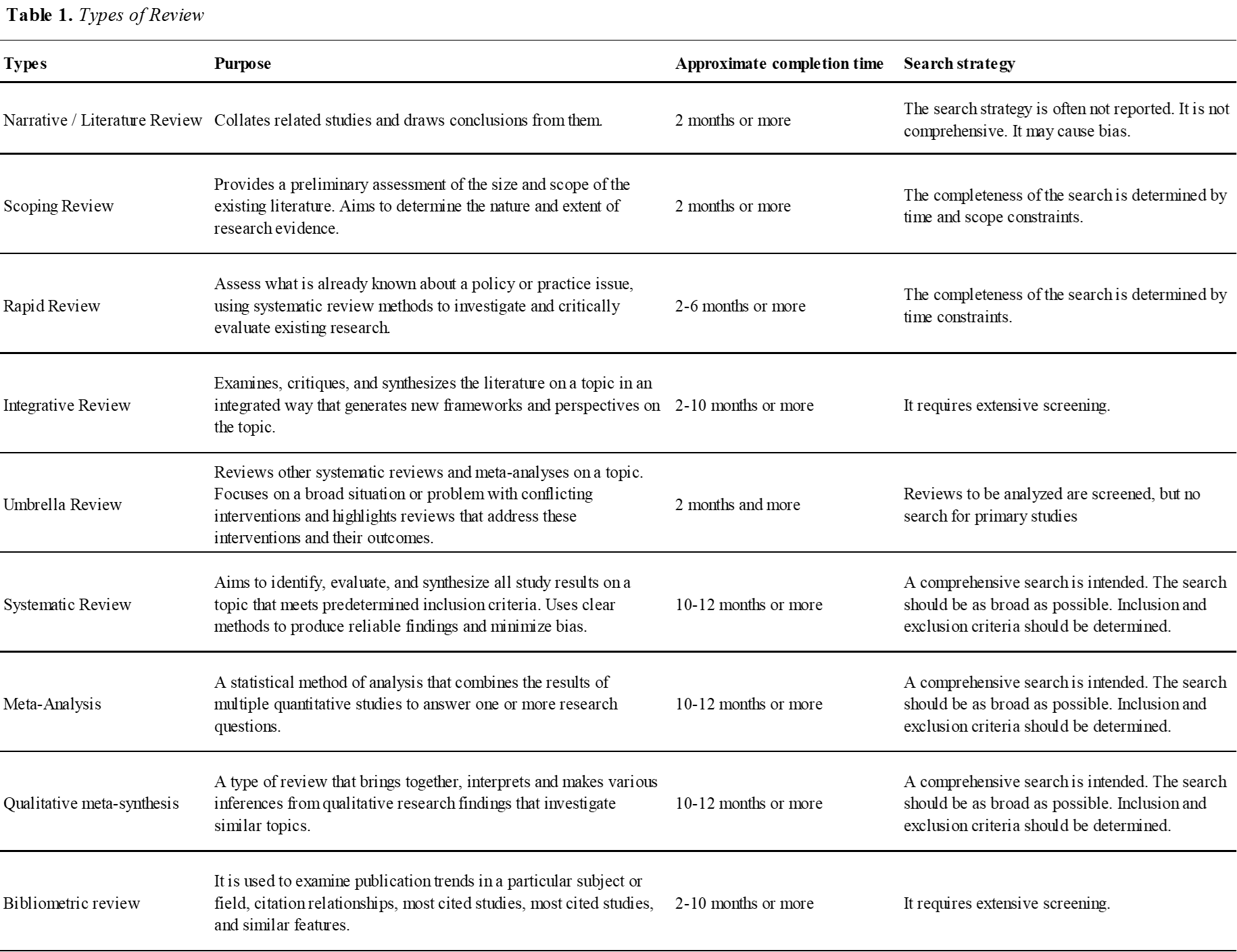
In Table 1, there is a resource intended to guide researchers by comparing the purposes, approximate completion times, and search strategies of different review types. Each type of review addresses research questions from a different perspective and offers different methods for gaining a deeper understanding of a particular research topic. It provides detailed information to help researchers choose the most appropriate examination method to suit their needs and research process. It also provides a clear overview of the characteristics of each review type, completion times, and search strategies, providing researchers with a framework for planning the research process. It helps researchers choose the examination method best suited to their research questions and goals while also allowing a comprehensive review and analysis of the research literature.